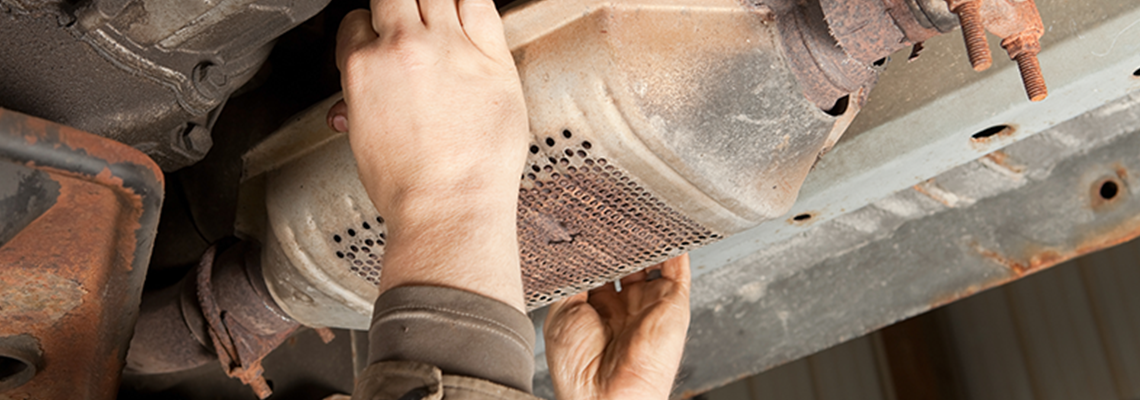
The catalytic converter is an important part of your car’s emission system.
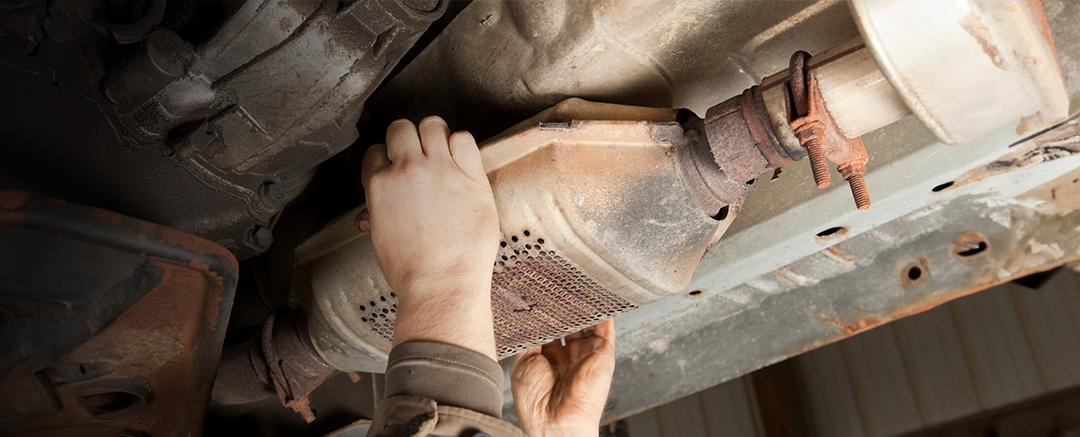
The catalytic converter’s main job is to convert car exhaust's bad emissions and pollutants into compounds that won’t harm the environment. In the metal canister itself, platinum and palladium — metals that act as chemical catalysts — coat a ceramic honeycomb or ceramic beads in the casing attached to the exhaust pipe.
Usually, a catalytic converter will last throughout the car’s lifetime, but sometimes it can go bad and will need replaced. Typically, this happens in older cars when the catalytic converter becomes clogged. As a result, the vehicle’s exhaust gases can’t get through to the muffler and then out of the car. Over time, your car can also use all the metals that act as the catalysts in the converter, which can cause the converter to fail.
How do you know if your catalytic converter needs to be repaired or replaced? Here are five common symptoms of a bad or failing catalytic converter.
#1: You fail your emissions test.
In most states, including Ohio, your vehicle’s emissions must be checked annually to make sure everything is working properly. The catalytic converter is your car's main component responsible for controlling engine emissions. An increase in the level of carbon emissions coming from your exhaust is a common sign that your catalytic converter may be failing. This can be from things like antifreeze or motor oil contaminating the chemical mechanisms inside the catalytic converter.
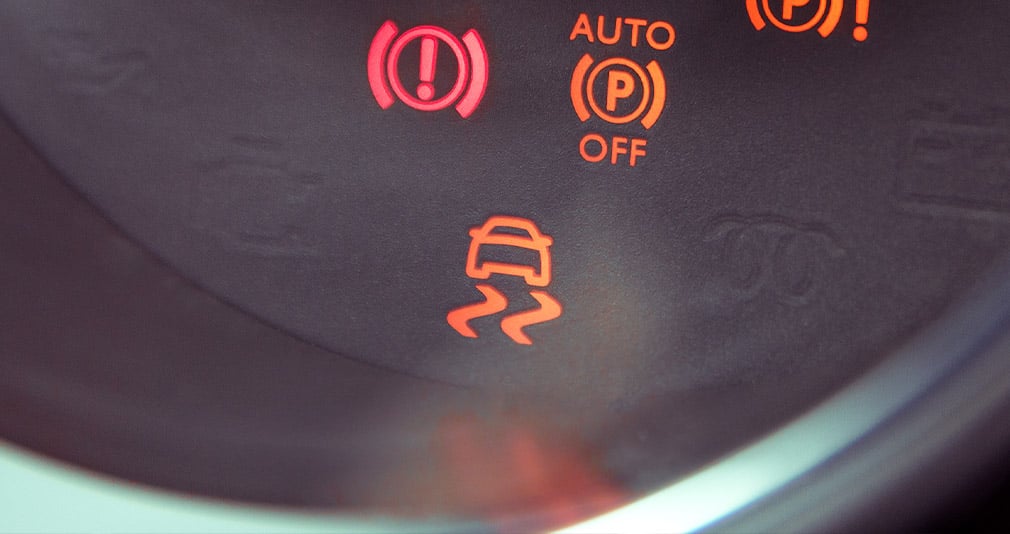
#2: Your check engine light is on.
Your on-board diagnostic system — which comes standard in all cars and trucks manufactured since 1996 — tests the catalytic converter automatically. Oxygen and air-to-fuel ratio sensors monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter by monitoring the gas levels in your exhaust. If too much pollution is coming out of your tailpipe, your check engine light will come on.
The most common reason for a catalytic converter to fail is because a related part fails — most often, a faulty spark plug. (Bad plugs can cause unburned gas to overheat inside the catalytic converter.) These plugs are inexpensive and easy to replace, so if you have a bad spark plug, be sure to take care of it before it causes damage. Read our blog post on the topic to learn how (and when) to change spark plugs.
#3: Fuel efficiency drops suddenly.
If you notice a sudden decrease in your gas mileage, it could be a sign of a clogged catalytic converter, or perhaps a faulty one. When your engine gets less oxygen — or when there is resistance in the exhaust path — your engine has to work harder, which ultimately consumes more fuel, causing you to get fewer miles to the gallon.
#4: When you push the gas pedal, you don’t go any faster.
Reduced engine performance is a red flag that there might be something wrong with your catalytic converter. When exhaust gets trapped in front of the catalytic converter, it can cause your engine to run less efficiently.
This increased back pressure can actually cause your engine to stall completely. Your vehicle may jerk or act as if there is an air lock in your system. Often, the car will feel like there is no fuel reaching the engine when you push the gas pedal.
#5: Your car doesn’t start easily — or at all.
If the catalytic converter is clogged and exhaust gases can’t get through to the muffler and out the back of the car, it can cause your engine to stall from increased exhaust back pressure. If your car runs normally for a few minutes after you start it, but then it starts sputtering or stalls out altogether, it could be your catalytic converter.
If you think your catalytic converter might be going bad, it’s important to have a mechanic take a look before the problem gets worse and leads to more extensive and expensive damage to your exhaust system. Your mechanic can check your emissions to see if the catalytic converter is clogged, or he can remove it and then check the change in your engine’s performance.
Sometimes, when a clogged converter is suspected, your mechanic can temporarily remove the oxygen sensor from the exhaust pipe in front of the catalytic converter and look for any changes in performance as a result.
The catalytic converter requires the right mix of exhaust gases at just the right temperature. Anything that causes the mixture or temperature to change can cause the converter to work less efficiently and fail faster.
Are you having trouble with your emissions and think it might be your catalytic converter? Are your exhaust sensors working properly? Stop by one of our six auto repair shops in Cleveland, Ohio today and have one of our experienced technicians take a look.